Exemplary Info About How Do You Write A Linear Line To Make Stacked Area Chart In Excel

General equation of a line.
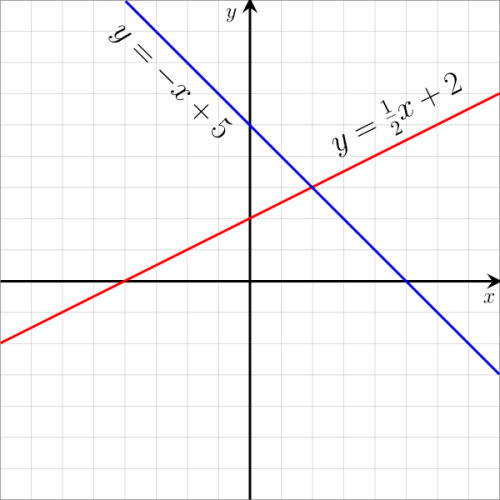
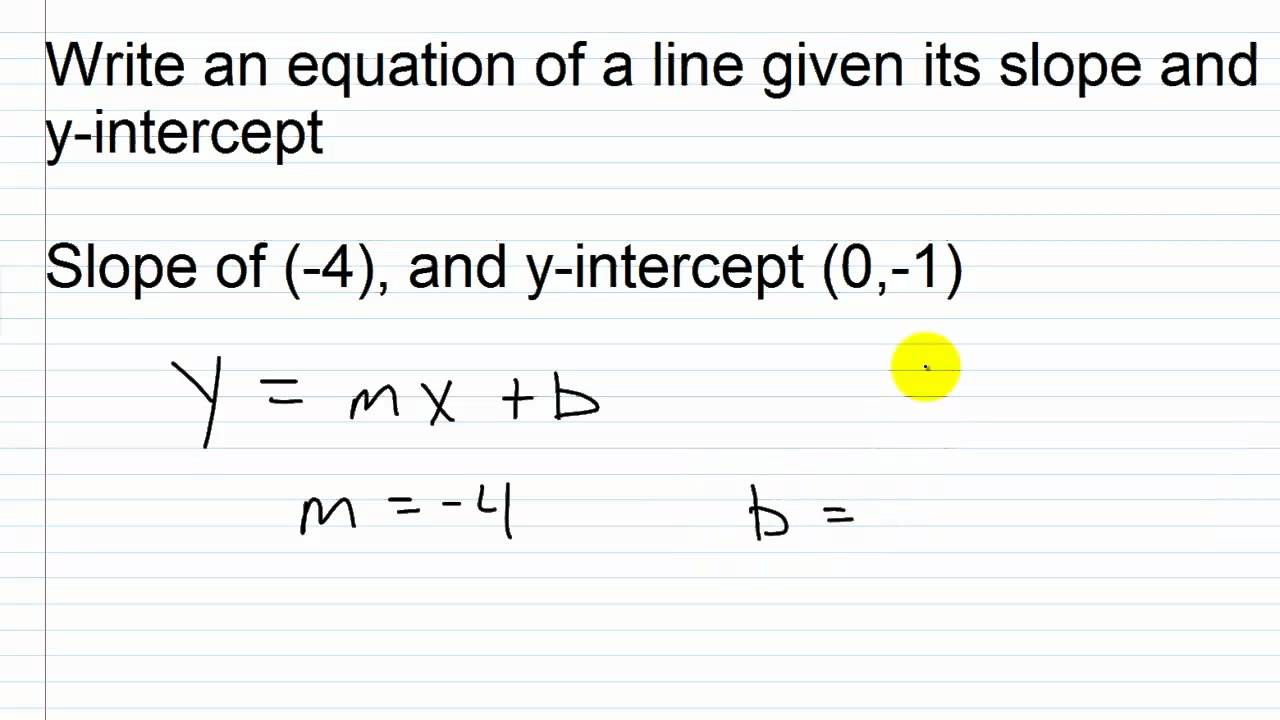
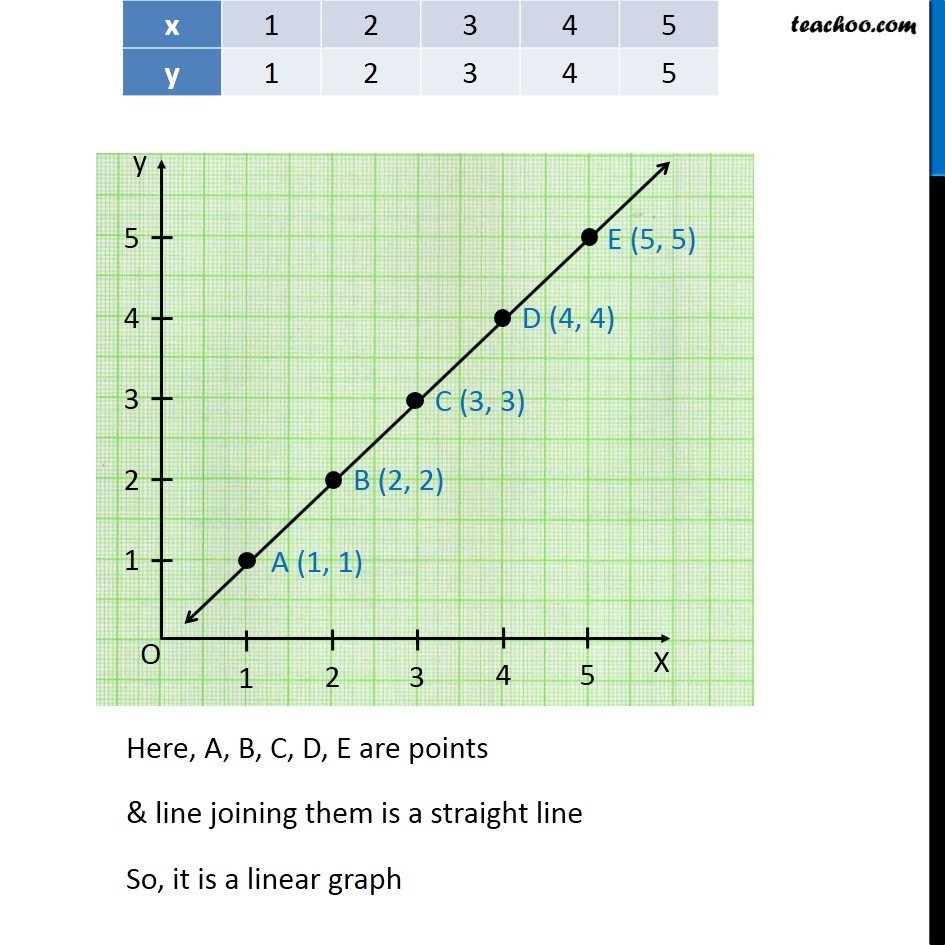
How do you write a linear line. Identify which parts of a linear equation are given and which parts need to be solved for using algebra. The equation of a straight line is usually written this way: Match linear functions with their graphs.
X = how far along. Write the equation of a line given the slope and a point on the line. Now let us see how to use it.
This form is also very useful when solving systems of two linear equations. Y = how far up. Find an equation of the line given the slope and a point.
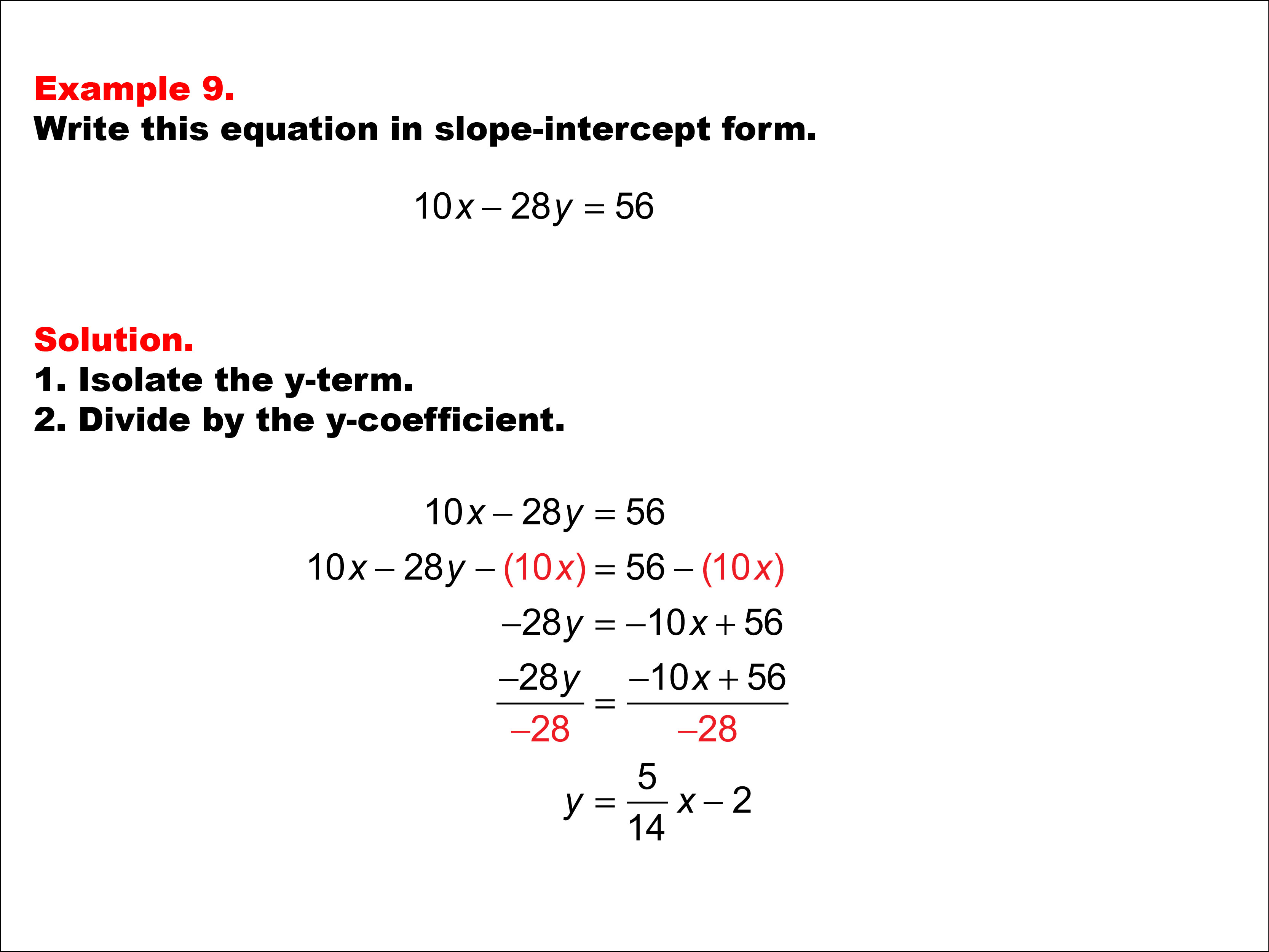
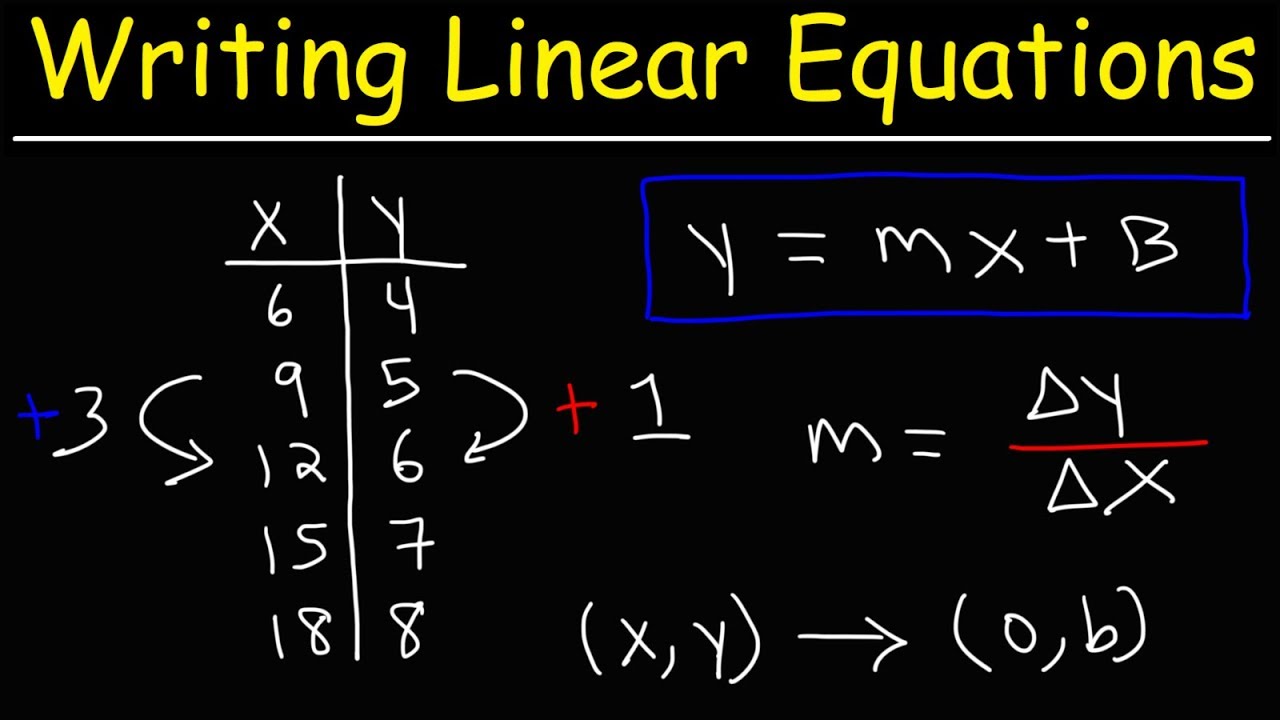
Let’s go over some examples of how to write the equation of a straight line in linear form [latex]y = mx + b[/latex]. Write the equation of a linear function given its graph. The standard form of a linear equation in one variable is of the form ax + b = 0.
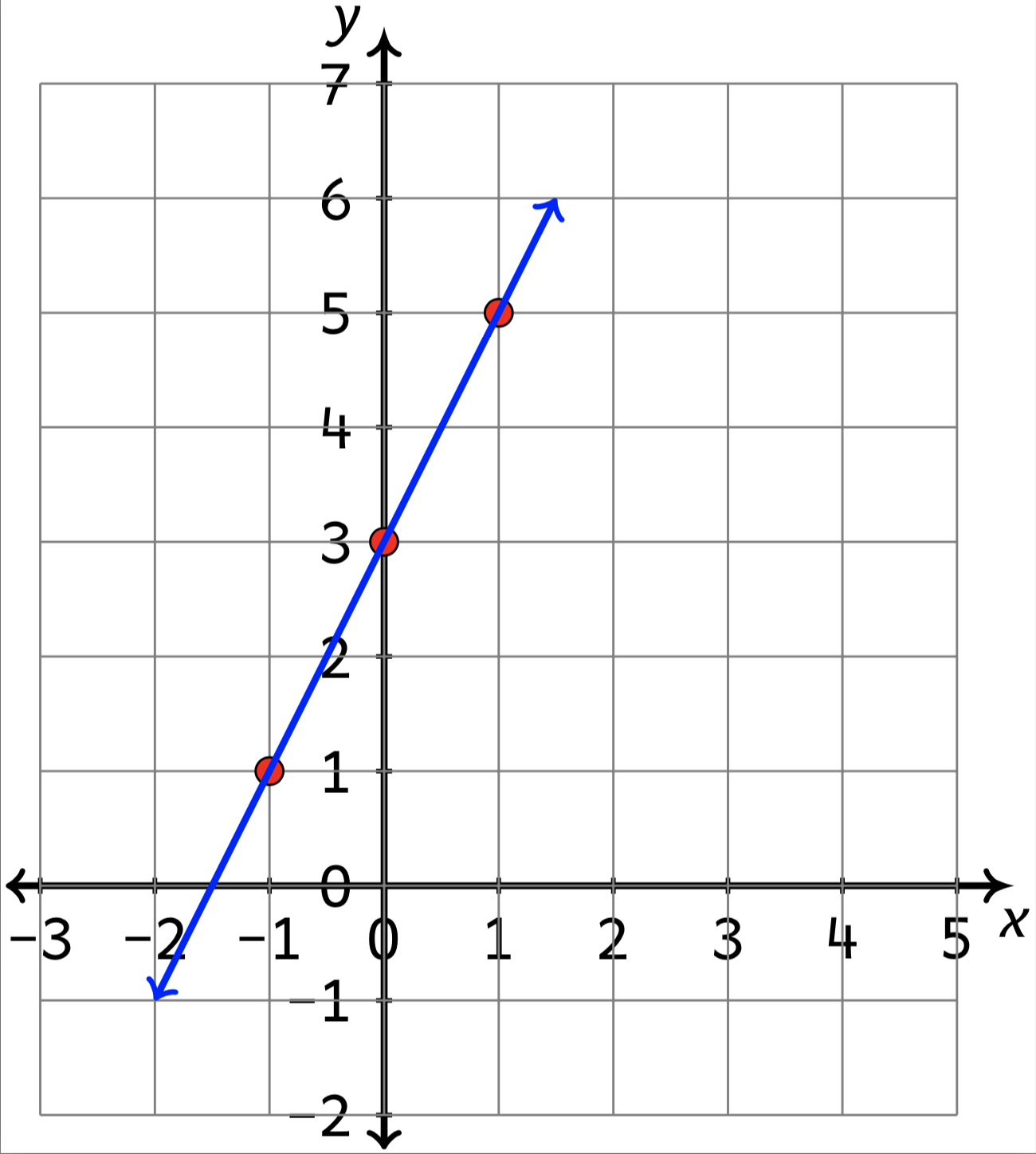
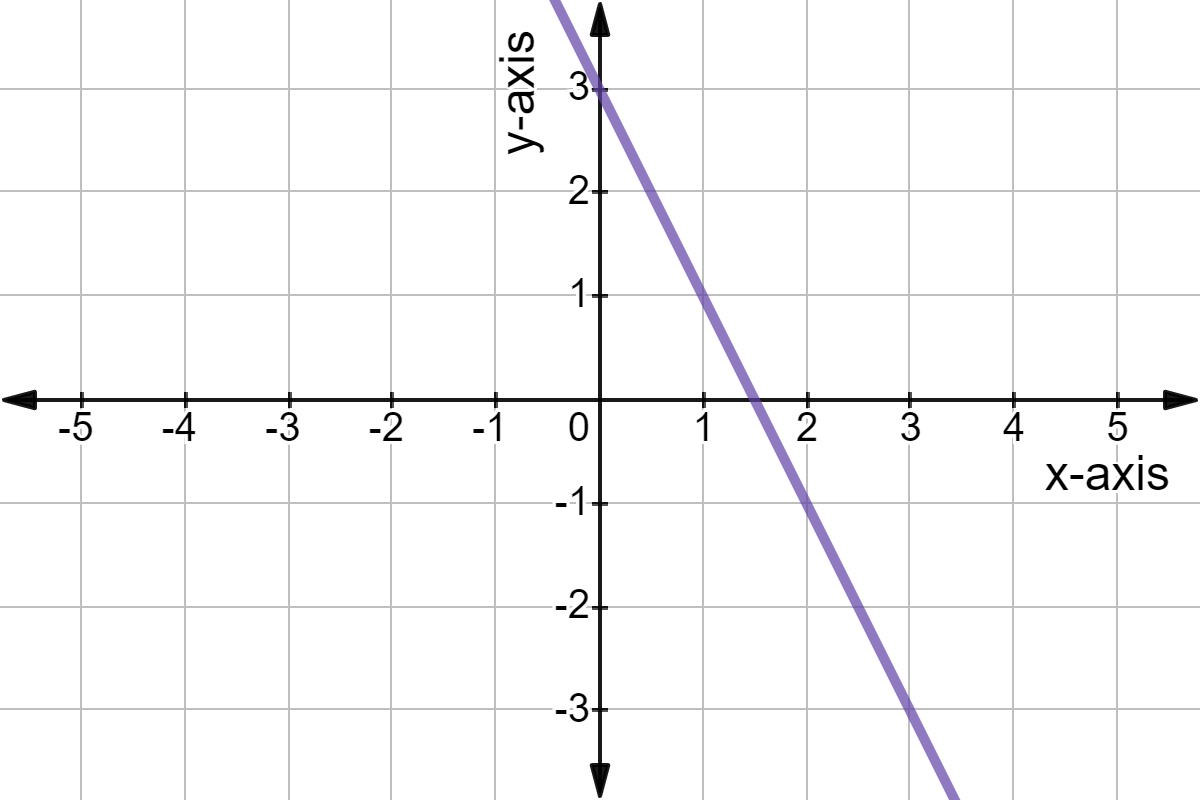
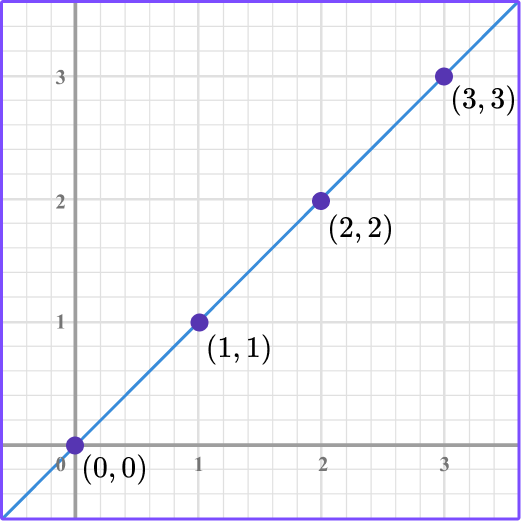
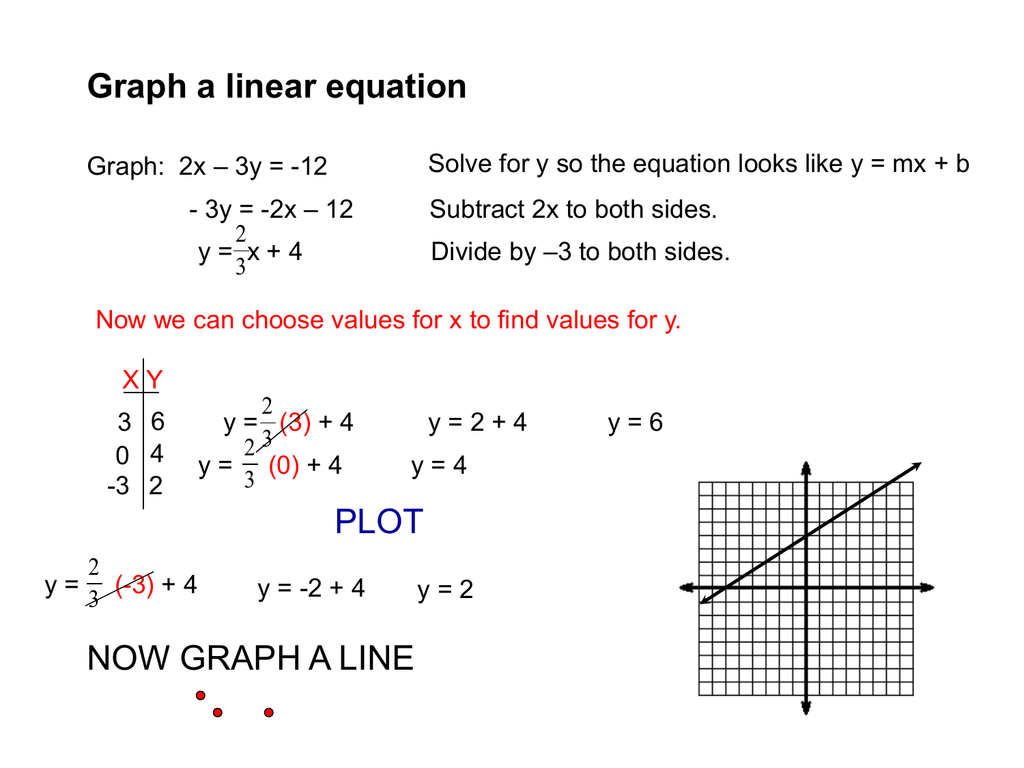
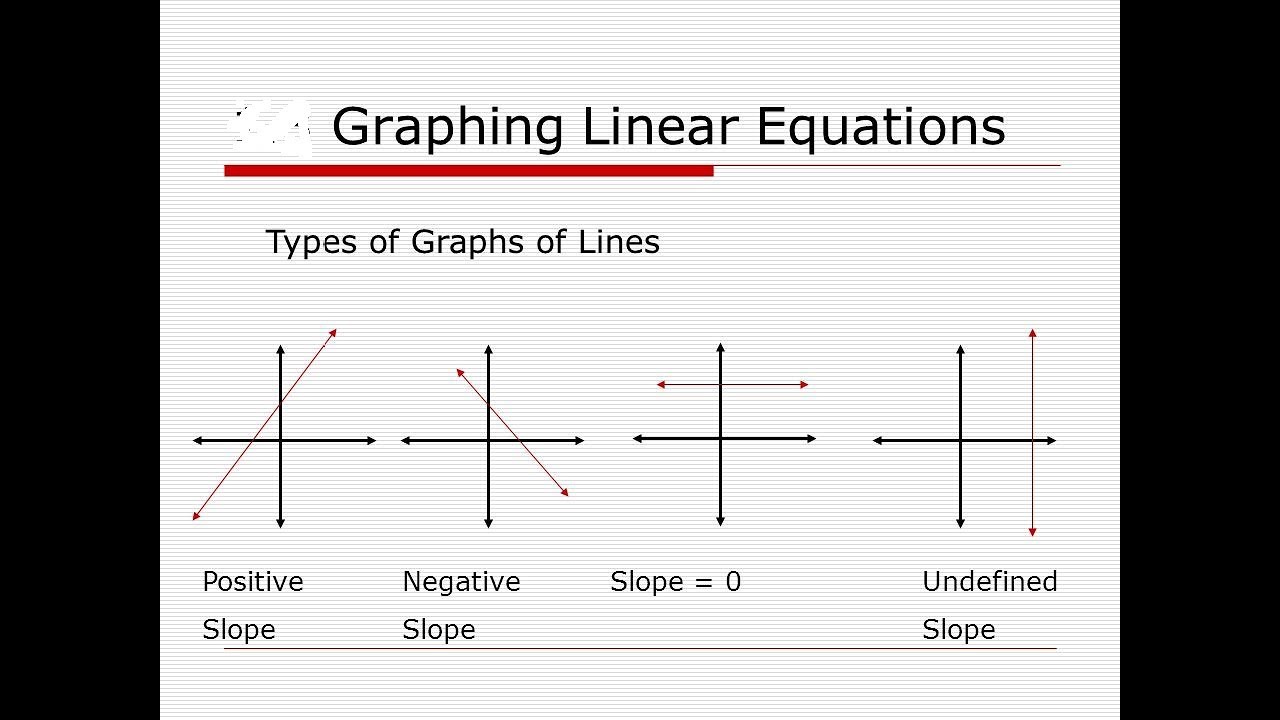
A linear equation is an equation for a straight line. The graph of y = 2x+1 is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, start by making sure the equation is in y = mx + b form.
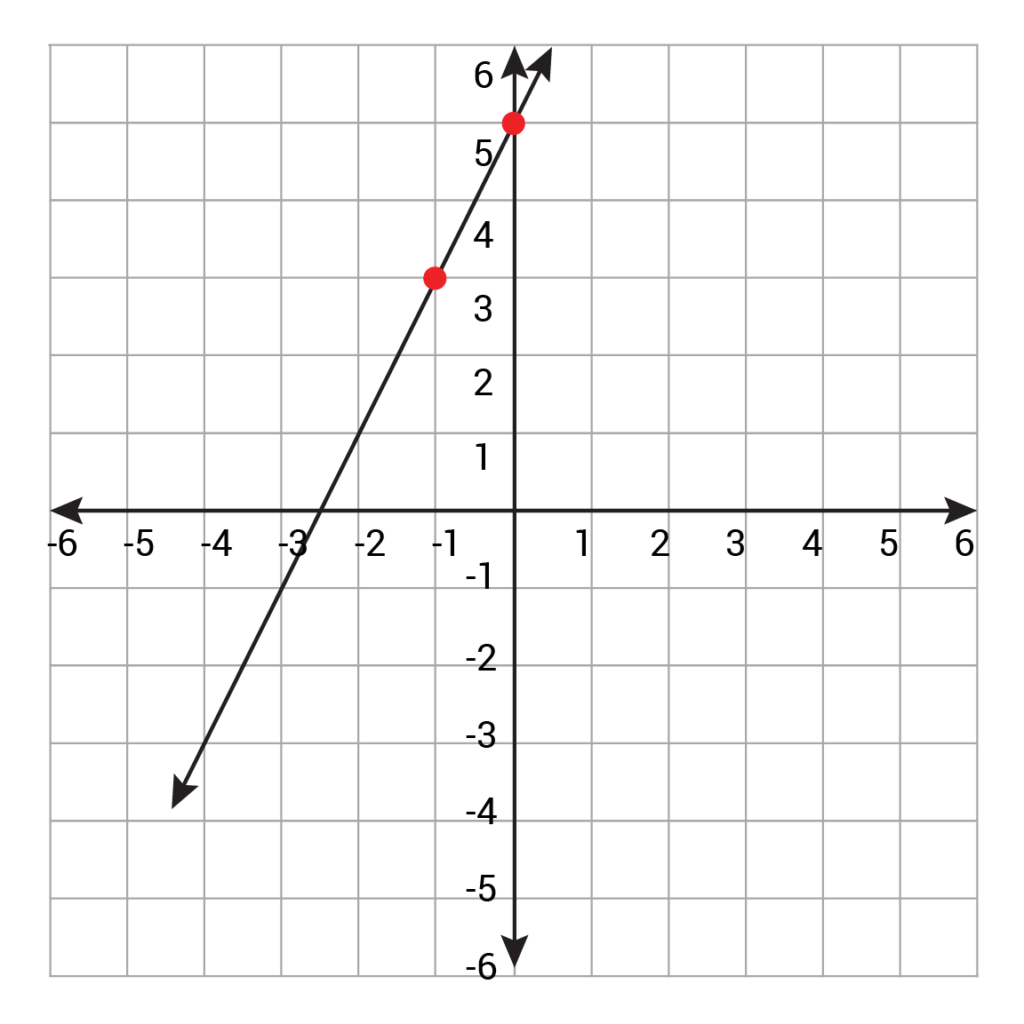
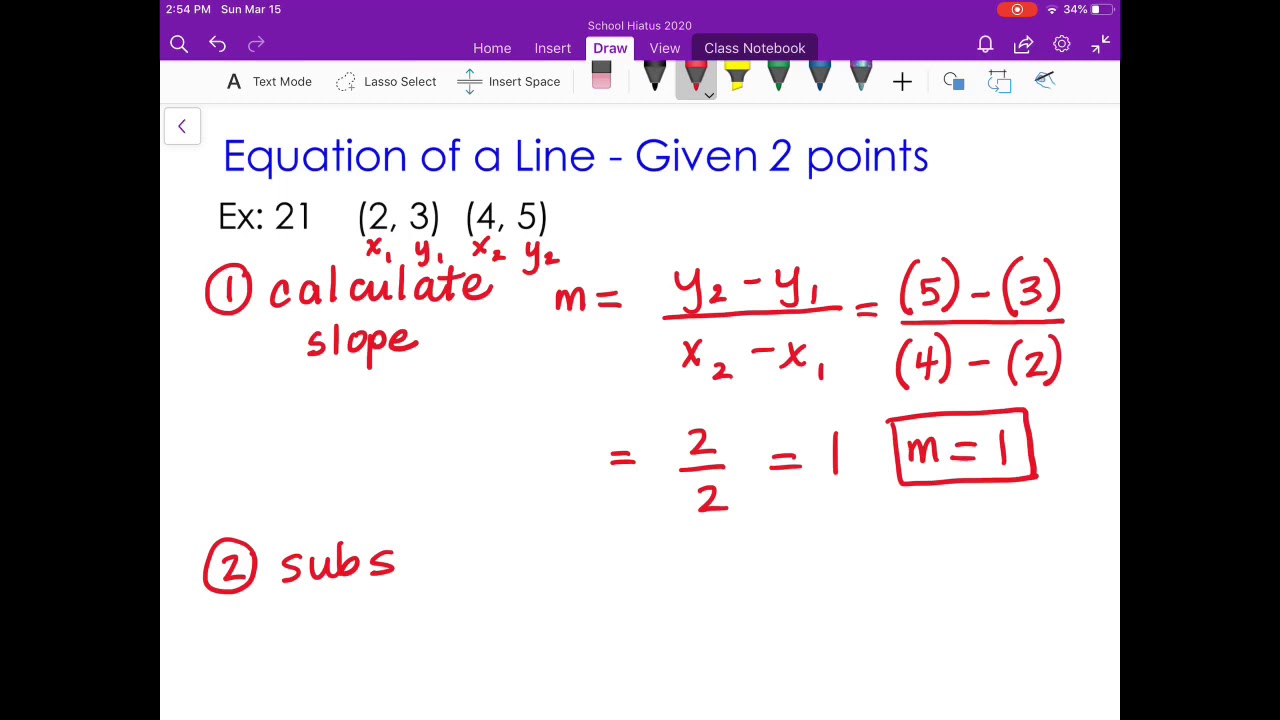
Slope m = change in y change in x = y − y1 x − x1. (x, y) is any other point on the line. Test your understanding of linear equations, functions, & graphs with these nan questions.
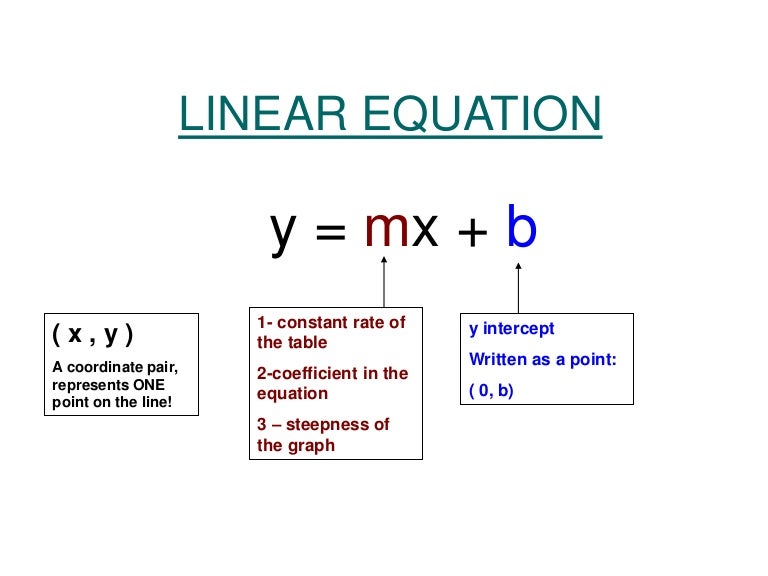
There are three main forms of linear equations. A linear equation is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is always 1. Y = mx + b.
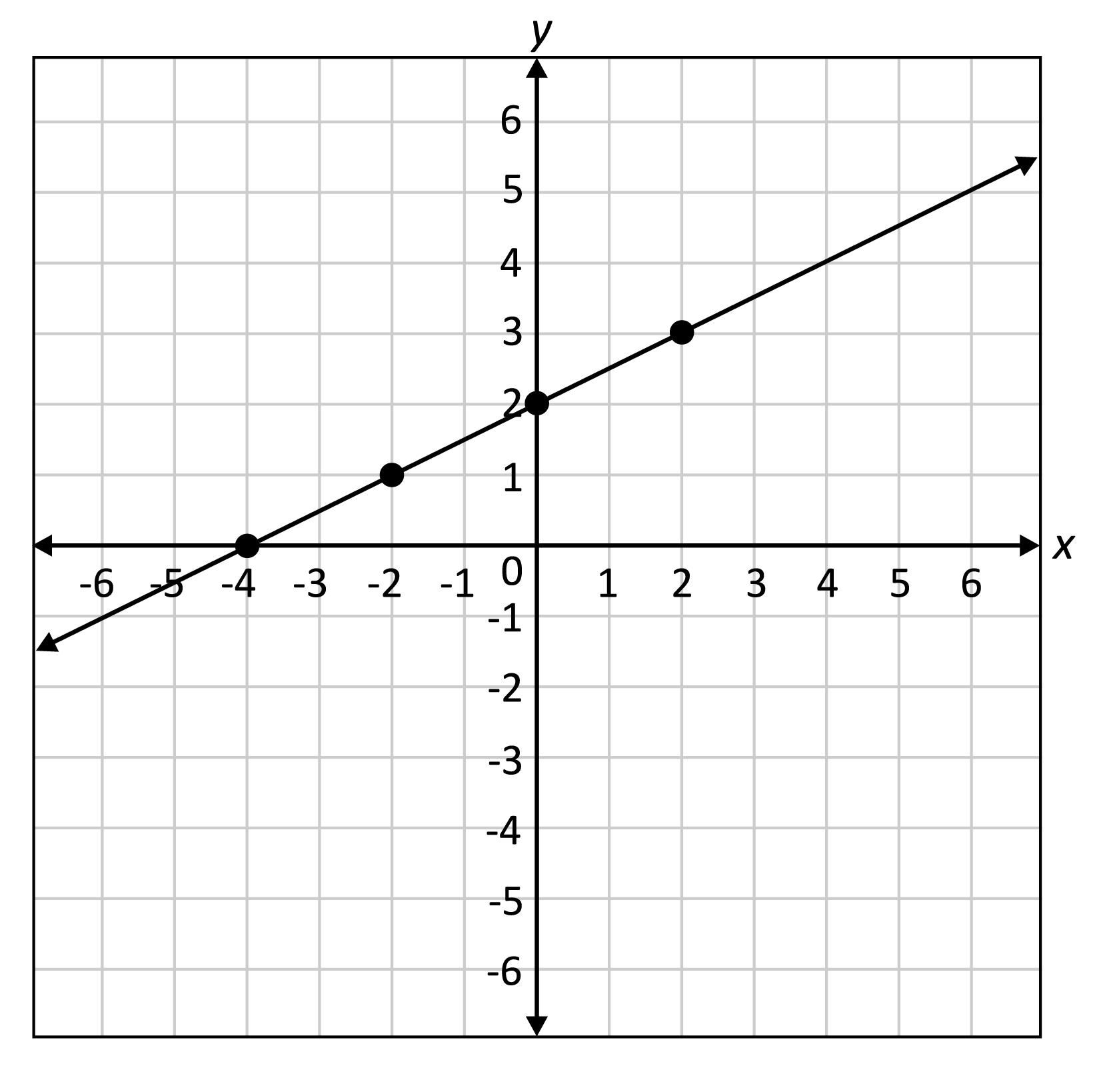
The standard forms of the equation of a line are: The graph of a straight line can be. This can be done by calculating the slope between two known points of the line using the slope formula.
Ax + by + c = 0. When x increases, y increases twice as fast, so we need 2x. A line passes through the points ( − 2, − 4) and ( − 5, 5).
The general form is not always the most useful form, and you may prefer to use: (or y = mx + c in the uk see below) what does it stand for? Writing linear equations in all forms.